

Currently, the key supporting components related to common cathode technology are LED diodes, power supplies, and driver ICs. ■ Common cathode technology reduces forward voltage drop by reducing the supply voltage of red LEDs, however, this requires the use of more power supplies, which further increases the complexity of the component layout on PCBs. By using common cathode technology, LED displays can reduce excessive heat and power consumption, pixel failure rate, and ghost lines (tailing effect), thus improving LED displays’ overall performance Supply chain

Moreover, there are no extra line-scanning devices needed to achieve this. ■ Based on accurate power control, common cathode technology can reduce the power consumption of the entire system by reducing the red LEDs’ supply voltage. Consequently, less heat is produced as less power is consumed. Because of this separate and precise power supply, the power efficiency is higher. ■ In common cathode mode, the LED display provides RGB LEDs with separate voltage based on actual needs (2.8V for the red LED, and 3.8V for the green and blue LEDs). ■ In common anode mode, the LED display provides RGB LEDs with a unified voltage higher than 3.8V (such as 5V), therefore the power consumption is high. The forward voltage drop is reduced, and as a result, there is less internal conduction resistance. Voltage and current are precisely distributed based on individual needs, then to the negative ends of ICs. ■ In common cathode mode, the LED display’s current first passes through LED diodes with R, G, and B LEDs separately powered.
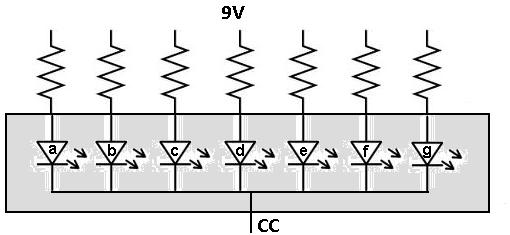
■ In common anode mode, the current of LED displays flows from PCB to LED diodes, and the RGB LEDs are powered with the same power source at the same power rate, and therefore the forward voltage drop is increased. The difference between the common cathode and common Anode Under line-scanning drive mode, LED displays can be categorized into two types: the common cathode and the common anode.Īs the name implies, common anode means individual LEDs are connected via their positive ends and driven by negative ends and common cathode means individual LEDs are connected via their negative ends and driven by positive ends, and in common cathode mode, R, G, B chips are separately powered with voltage and current precisely distributed to red, green, and red diodes, and the current passes the diodes then to the negative ends of ICs. However, when LED displays began to be used for indoor applications using smaller pitch products, the space available for electronic components was squeezed, and as a result, dynamic scan drive (line-scanning drive) based on time-division multiplexing (TDM) came into being. In the early stage, LED displays were mostly used for outdoor applications using larger pitch products, which did not have a physical space limit for driver ICs as they were designed with static scan drive. With an independent voltage power supply, the red, green, and blue LED chips can be separately and accurately powered, providing different voltages to them under the same current, which can ensure that they work at their rated power, thereby improving energy utilization and reducing energy consumption.Ĭommon Cathode VS Common Anode LED display, which is better? LED professionals know that the rated power required for the red, green, and blue chips is different, and ordinary power supply methods cannot separate them and can only provide them with the same power. Additionally, this technology can separate and precisely power the red, green, and blue LED chips. The voltage drop and current loss can be reduced by using the independent voltages power supply method. It is an energy-saving power supply technology for LED displays where the current first passes through the LED chips and then reaches the negative pole of the driving IC, hence the name “common cathode”. A common cathode LED screen has all of the cathodes of the individual LEDs connected together and to a common terminal, while the anodes of each LED are connected separately.Ĭommon cathode”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
